23.02.2021
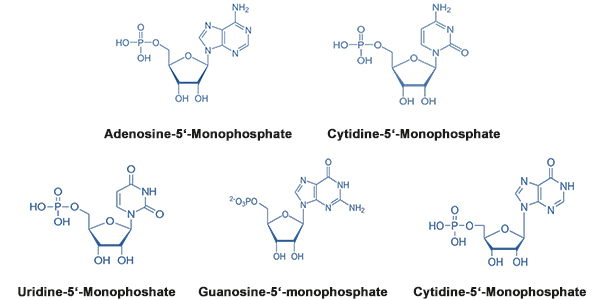
5'- Mononucleotides
Nucleotides are composed of a base moiety (purine or pyrimidine) and a pentose whose 5'-position is phosphorylated.
They are components of various coenzymes and thus involved in the regulation of numerous metabolic processes. Furthermore, they form the building blocks of nucleic acids, RNA as well as DNA.
Nucleotides do not belong to the essential nutrients. In phases of growth, however, the requirement may be increased, which is why nucleotides, among other things, may be added to infant formula and follow-on formula (in accordance with Regulation (EU) No 609/2013).[1][2]
According to Art. 1 of Regulation (EU) 2016/127, infant formulae and follow-on formulae may only be placed on the market if they comply, inter alia, with the specifications of this Regulation. (see table)
Maximum levels for nucleotides
| Nucleotides | Maximum level (1) | |
| (mg/100 kJ) | (mg/100 kcal) | |
| Cytidine-5‘-monophosphate (CMP) | 0.60 | 2.50 |
| Uridine-5‘-monophosphate (UMP) | 0.42 | 1.75 |
| Adenosine-5‘-monophosphate (AMP) | 0.36 | 1.50 |
| Guanosine-5‘-monophosphate (GMP) | 0.12 | 0.50 |
| Inosine-5‘-monophosphate (IMP) | 0.24 | 1.00 |
| (1) The total concentration of nucleotides shall not exceed 1.2 mg/100 kJ (5 mg/100 kcal). | ||
Analytics
A new method for the determination of 5'-mononucleotides has been established at the Institute for Product Quality. For this purpose, they are purified in infant formula and follow-on formula by means of a strong anion exchange solid phase extraction and identified and quantified by means of high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a diode array detector (HPLC-DAD).
We will be happy to advise you. Contact us for more information.
Source:
1 Michal G.; Biochemical Pathways, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag GmbH Heidelberg
2 Rehner G., Daniel H.; Biochemie der Ernährung, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag GmbH Heidelberg (Auflage 3)

